Playing with Github Actions
After using Azure DevOps Yaml Pipelines for some time now I wanted to learn more about Github’s Actions.
Introduction
According to the Github documentation, GitHub Actions makes it easy to automate all your software workflows, with world-class CI/CD.
Sounds interesting, let’s explore more about Github Actions in this blog post.
Github Action terminology
Before we dive into the Github Actions we first need to know more about the terminology used when working with Github Actions.
Workflows
Workflows are custom automated processes that you can set up in your repository to build, test, package, release, or deploy any project on GitHub.
Workflow jobs
A workflow job is a defined task made up of steps.
Workflow runs
A workflow run is an instance of your workflow that runs when the pre-configured event occurs.
Runners
The runner is the application that runs a job from a GitHub Actions workflow. The runner can run on the hosted machine pools or run on self-hosted environments.
Actions
Actions are individual tasks that you can combine to create jobs and customize your workflow. You can create your own actions, and use and customize actions shared by the GitHub community.
Marketplace
GitHub Marketplace is a central location for you to find actions created by the GitHub community.
You can discover new actions from the workflow editor on GitHub, and from the GitHub Marketplace page.
Get started
To get started with Github actions go to your Github Account open or create a new Repository and click on Actions tab.
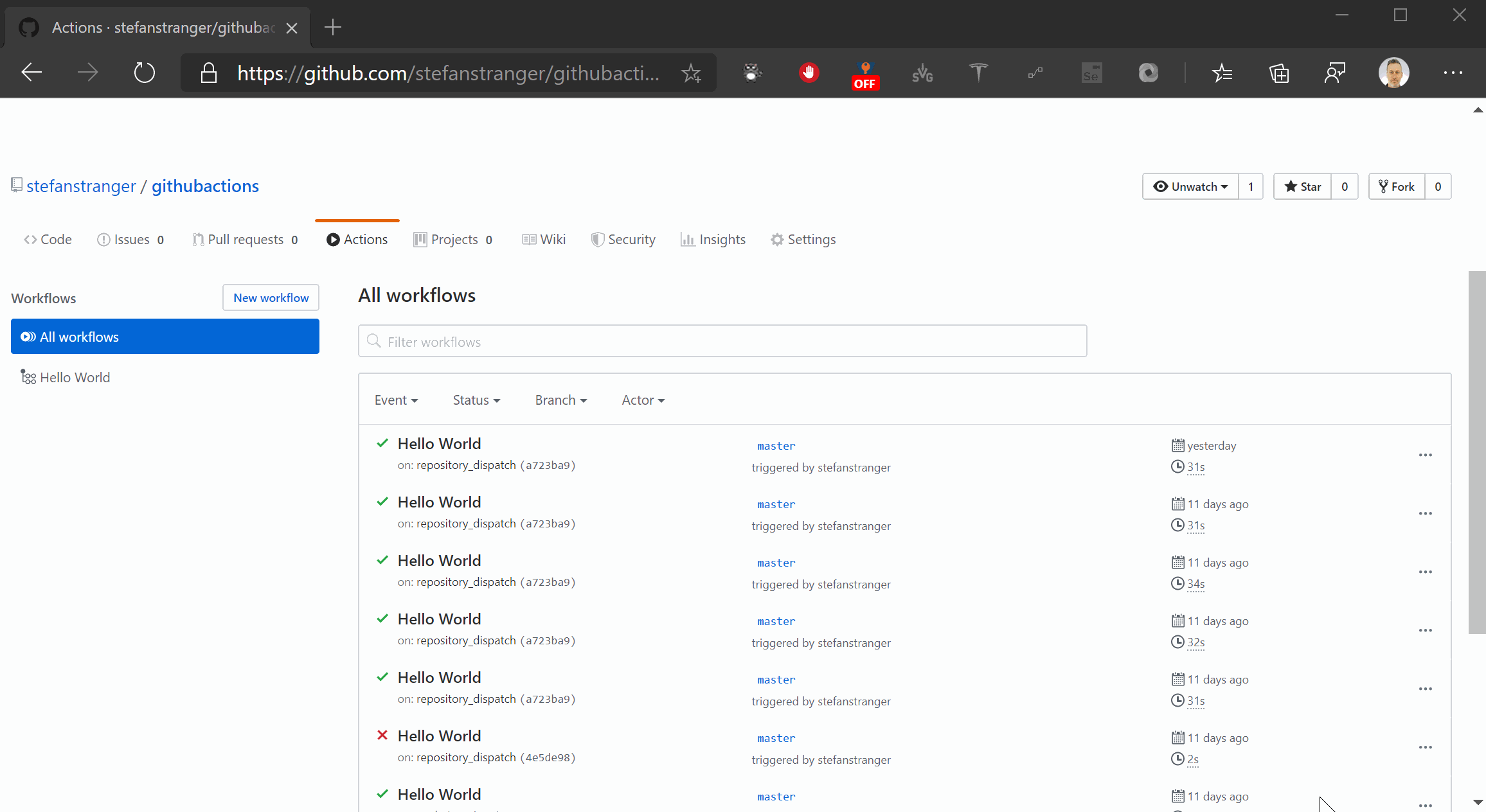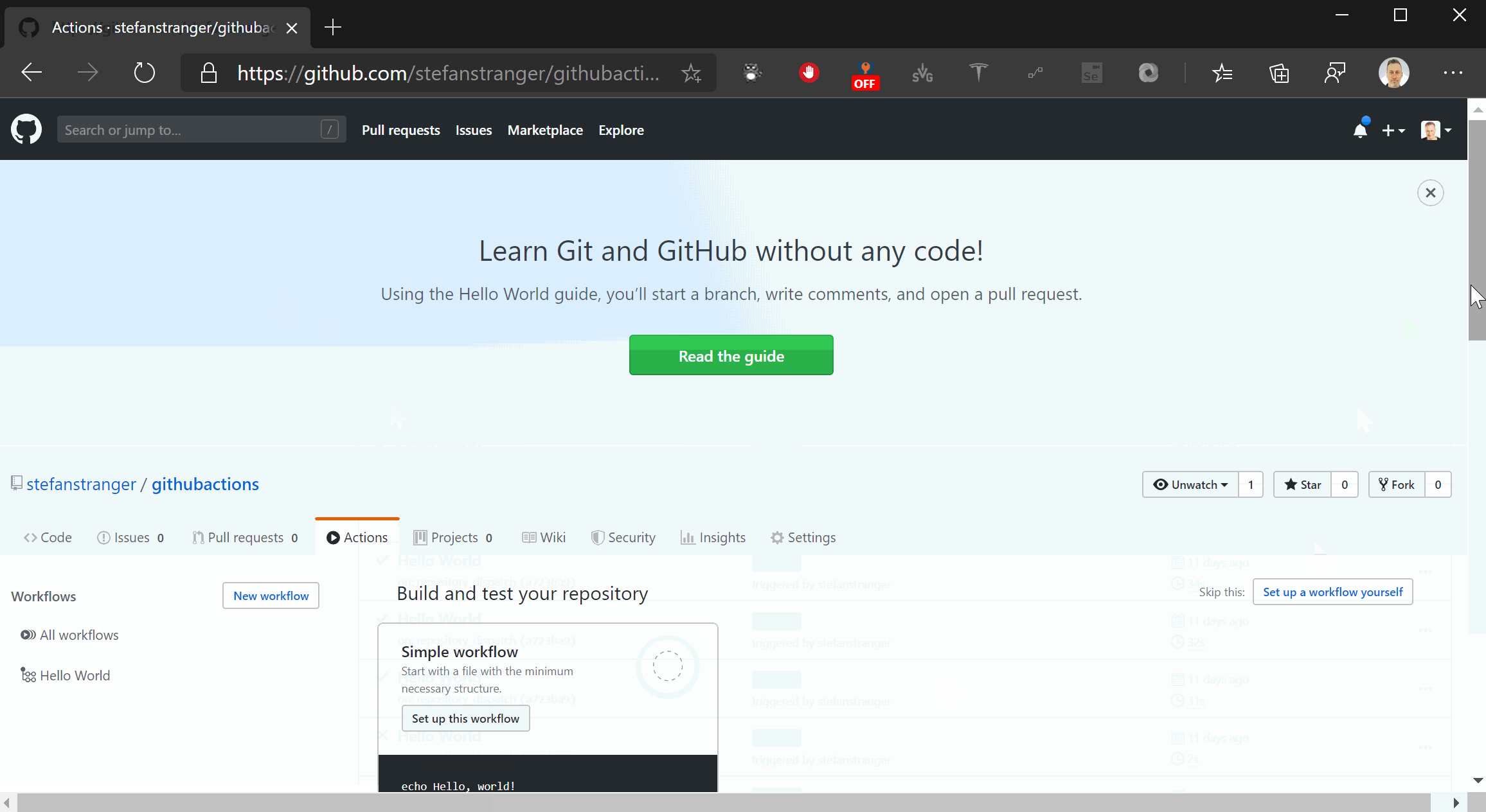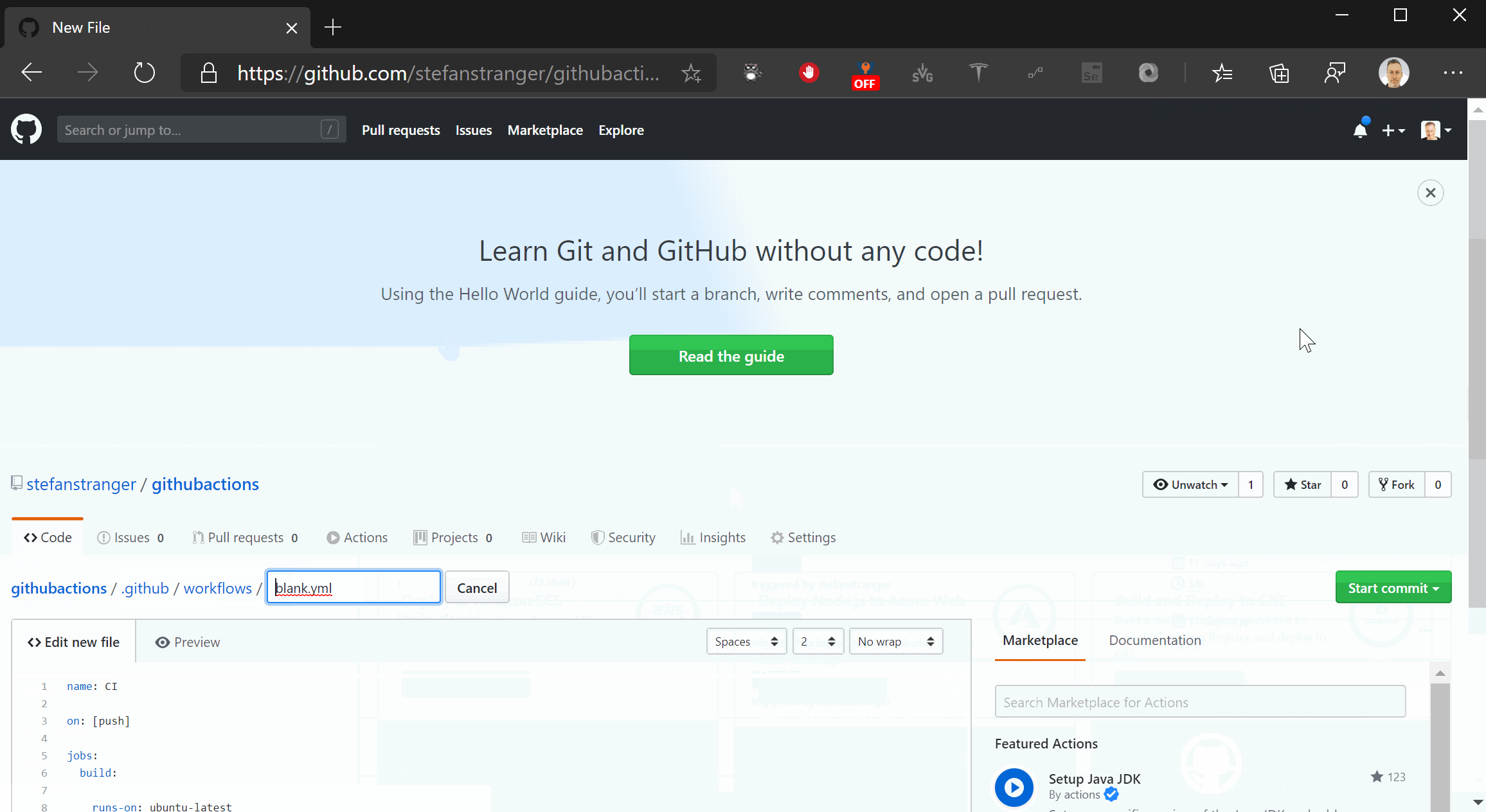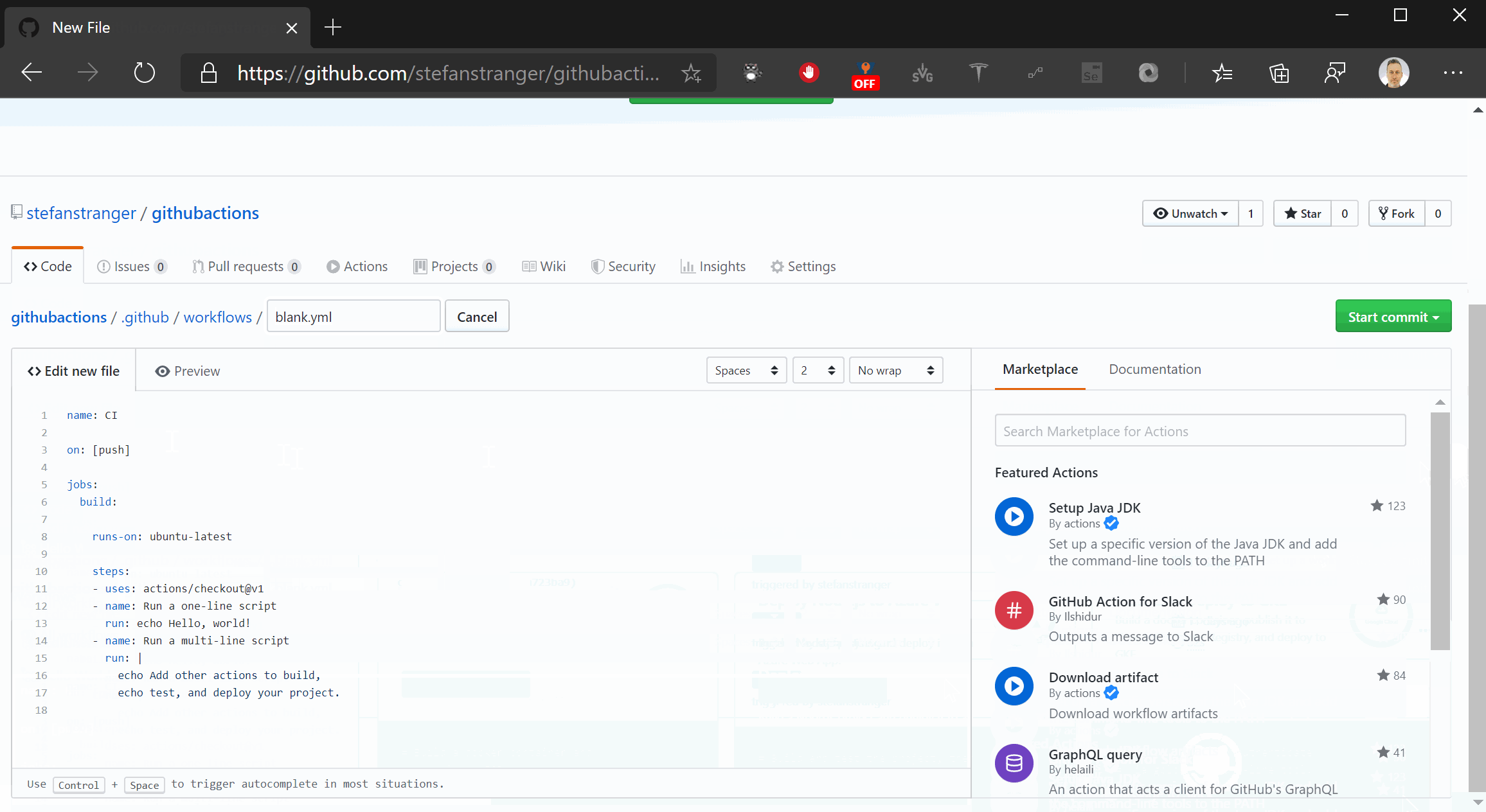
If you select the simple workflow you get below Hello World workflow.
name: CI
on: [push]
jobs:
build:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v1
- name: Run a one-line script
run: echo Hello, world!
- name: Run a multi-line script
run: |
echo Add other actions to build,
echo test, and deploy your project.
Let’s change this to a Hello World PowerShell version which can be triggered via a external webhook:
name: Hello World
on: [repository_dispatch]
jobs:
hello-world:
runs-on: windows-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v1
- name: Run PowerShell Hello World script
if: github.event.action == 'inline'
run: Write-Output 'Hello World!'
- name: Run a multi-line PowerShell script
if: github.event.action == 'inline'
run: |
$psversiontable;
Get-Process;
Result when above Github Action workflow is run:
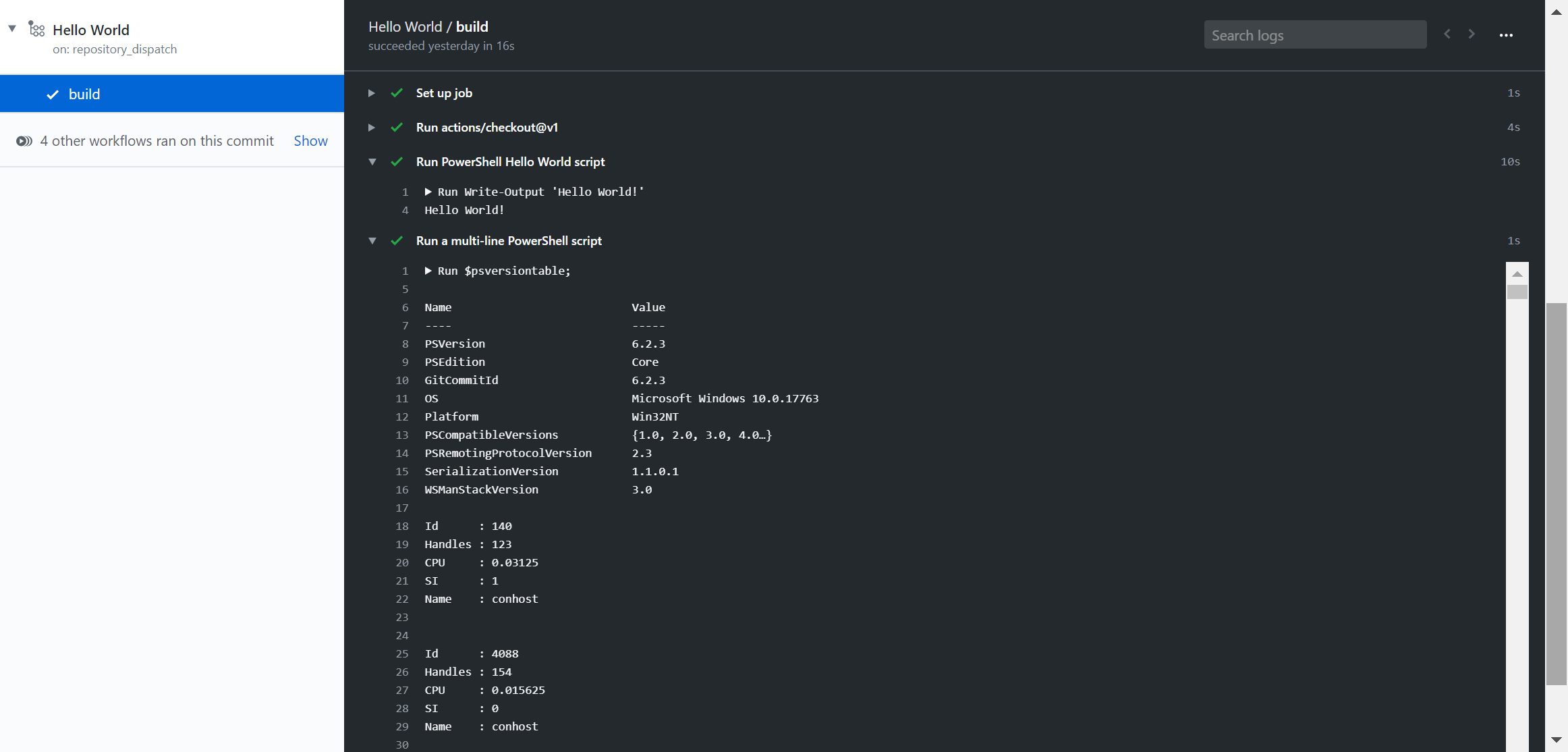
Explanation of Workflow
| Property | Description | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| name | The name of your workflow | |
| on | The name of the GitHub event that triggers the workflow | You can use the GitHub API to trigger a webhook event called repository_dispatch when you want to trigger a workflow for activity that happens outside of GitHub. |
| jobs | A workflow run is made up of one or more jobs | |
| hello-world | Name of the Job | |
| runs-on | Specifies the GitHub-hosted runner | On the windows-latest runs PowerShell Core version 6.2.3 |
| steps | ||
| uses | This action (actions/checkout@v1) checks-out your repository under $GITHUB_WORKSPACE, so your workflow can access it. | |
| name | Name of the step | |
| run | Run commands | Run PowerShell cmdlet ‘Write-Host’ |
| if | conditional to prevent a step from running unless a condition is met | the body of the web request to the Github action contains event_type=inline |
Trigger Github Action from webhook
By using the repository_dispatch type of trigger we can trigger the Github Actions via a Webhook.
To be able to trigger a Github Action from a webhook you need to create a Personal Access Token under Developer Settings.
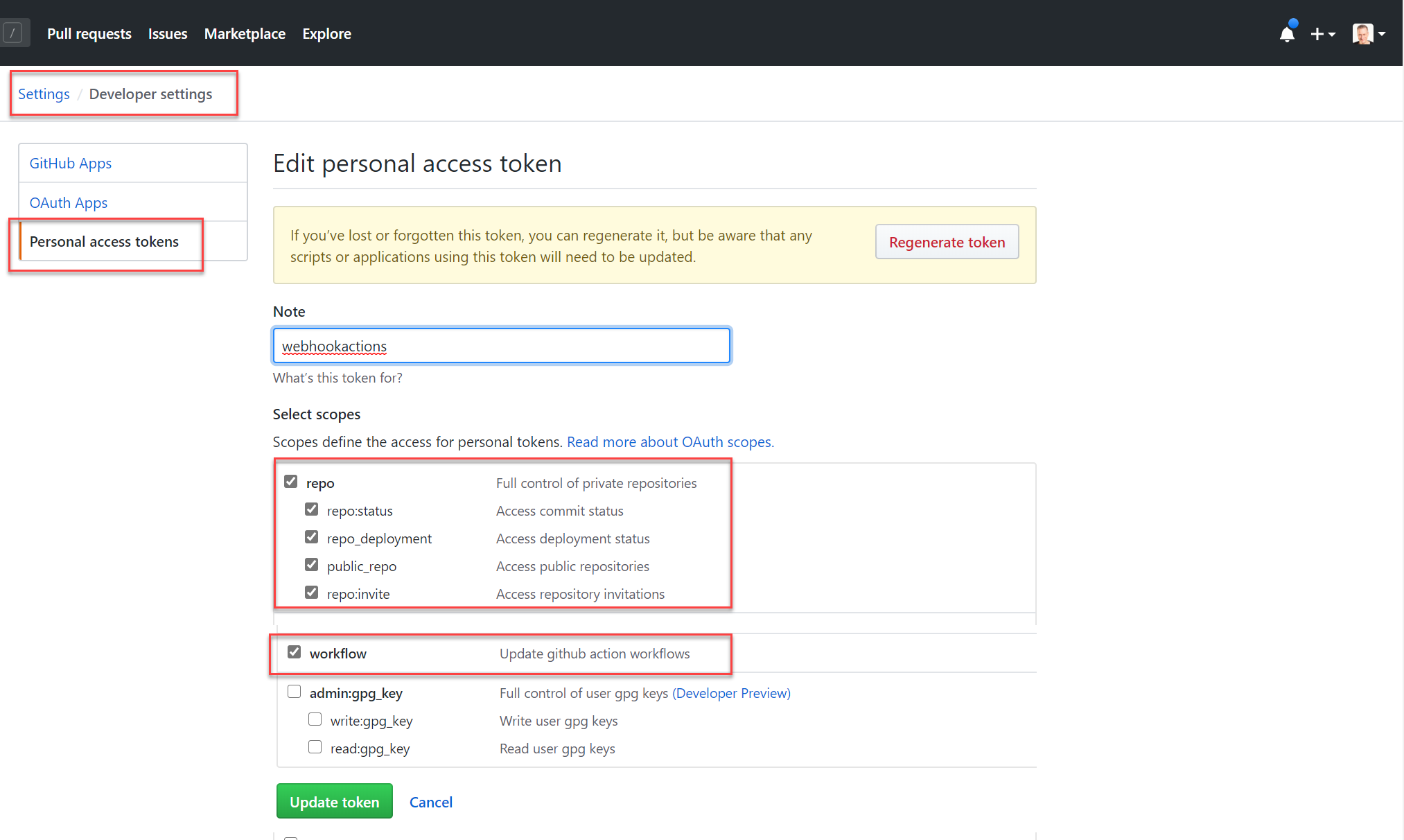
After storing the Github Personal Access Token as environment variable you can use this token in the web request.
<#
Triggering Github Actions from a webhook call
#>
#region variables
$GithubToken = $env:githubtoken # Personal Access Token stored as environment variable
$GithubUserName = 'stefanstranger'
$GithubRepo = 'githubactions'
#endregion
$uri = ('https://api.github.com/repos/{0}/{1}/dispatches' -f $GithubUserName, $GithubRepo)
#region web request call
$Body = @{
'event_type' = 'inline' #used in the if condition of the Github Action
} | ConvertTo-Json
$params = @{
ContentType = 'application/json'
Headers = @{
'authorization' = "token $($GithubToken)"
'accept' = 'application/vnd.github.everest-preview+json'
}
Method = 'Post'
URI = $Uri
Body = $Body
}
Invoke-RestMethod @params -verbose
#endregion
If you run above PowerShell script it should trigger the earlier configured Github Action.
Run a PowerShell script stored in your Repository
Instead of an inline PowerShell script we can also use a PowerShell script from our Repository.
Check the following Hello-World.ps1 example script.
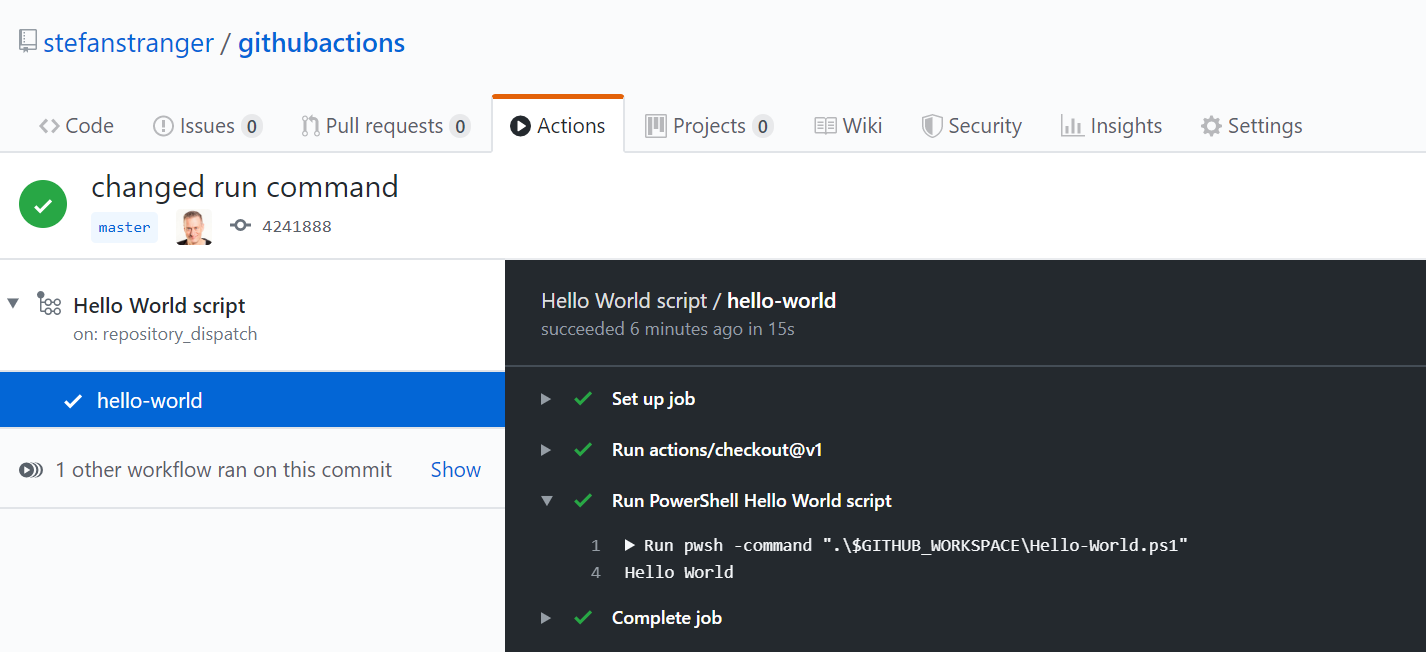
If we want to run this script from our Github Action we can create the following Github Action.
name: Hello World script
on: [repository_dispatch]
jobs:
hello-world-script:
runs-on: windows-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v1
- name: Run PowerShell Hello World script
if: github.event.action == 'script'
run: pwsh -command ".\$GITHUB_WORKSPACE\Hello-World.ps1"
Result:
In my next blog post I want to investigate the Github Marketplace and explain how to develop and publish Github Actions.
References:
- Github Actions documentation
- Help documentation Github Action
- A curated list of awesome things related to GitHub Actions
- Workflow syntax for GitHub Actions
- Github repo used for blog post