What are AI LLM Agents?
Introducing AI LLM Agents: The Future of Intelligent Automation
After watching Doug Finke’s YouTube video called “Build Autonomous Agents in PowerShell with PSAI Agent Real-Time Data Integration” I got interested in the topic of Large Language Model (LLM) Agents. Especially the topic about Function Calls got me excited to learn more.
In this blog post, I will explore what LLM Agents are, their functionality and demo them using one of the LLM Agent frameworks called AutoGen.
What are LLM Agents?
An LLM agent is a system that autonomously performs tasks by planning its task execution and utilizing available tools. LLM Agents leverage large language models to understand and respond to user inputs step-by-step and decide when to call external tools.
Key Features of LLM Agents:
- Natural Language Understanding: LLM Agents can comprehend complex queries and context, enabling them to generate relevant responses.
- Context Awareness: These agents maintain context throughout a conversation, allowing for more engaging and coherent interactions.
- Task Automation: LLM Agents can automate repetitive tasks, freeing up human resources for more complex endeavors.
- Learning and Adaptation: The capability to continuously learn from new data ensures that LLM Agents remain up to date and improve over time.
In AutoGen, an agent is an entity that can send and receive messages to and from other agents in its environment. An agent can be powered by models (such as a large language model like GPT-4), code executors (such as an IPython kernel), human, or a combination of these and other pluggable and customizable components.
What are LLM Agents used for?
1. Customer Support
LLM Agents can serve as virtual customer service representatives, addressing FAQs, troubleshooting issues, and providing seamless support, enhancing customer experience while reducing wait times.
2. Content Creation
Businesses can leverage LLM Agents for generating high-quality content, from blog posts to marketing materials, optimizing their content strategies and reducing the time required for manual creation.
3. Personal Assistants
These agents can function as personal assistants, helping individuals schedule appointments, manage emails, and perform day-to-day tasks, leading to improved productivity.
4. Education and Tutoring
LLM Agents can facilitate personalized learning experiences, acting as tutors that adapt to the specific needs of students, provide explanations, and answer queries.
5. Data Analysis
LLM Agents can analyze vast amounts of data, extracting key insights and presenting them in an understandable manner, aiding in business decision-making processes.
Key Components of an LLM Agent
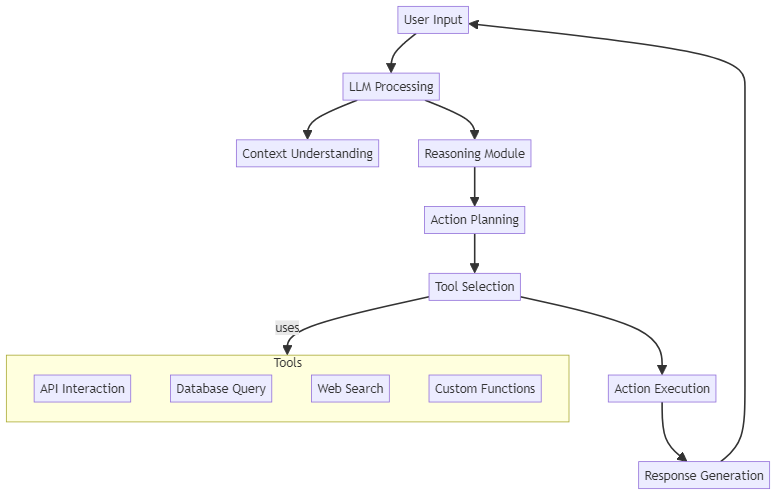
Explanation of Components:
- User Input: The initial input provided by the user, which can be a question, command, or request.
- LLM Processing: The process where the large language model analyzes the input.
- Context Understanding: The LLM interprets the context of the user input for more accurate responses.
- Reasoning Module: This component enables the LLM to reason through the problem presented.
- Action Planning: The agent creates a plan based on the reasoning module.
- Tool Selection: The agent determines which external tools or APIs (Function Calling) to use to fulfill the user request.
- Action Execution: The selected tools are used to perform specific actions.
- Response Generation: Finally, the agent generates a response based on the actions taken.
Challenges and Considerations
While the prospects of LLM Agents are promising, there are challenges that need to be taken into consideration:
- Bias and Fairness: LLMs are trained on large datasets that may contain biases, leading to skewed outputs. Continuous efforts are needed to ensure fairness in AI-generated responses.
- Data Privacy: Safeguarding user data is critical, and developers must adhere to privacy regulations while training and implementing LLM Agents.
- Dependence and Job Displacement: While LLM Agents can automate tasks, it’s essential to consider the impact on employment and find a balance between automation and human involvement.
AutoGen Framework
This is an Open-Source Programming Framework for Agentic AI. AutoGen provides multi-agent conversation framework as a high-level abstraction. With this framework, you can conveniently build LLM workflows. There are multiple LLM Agent frameworks or platforms but I choose AutoGen because it’s developed by Microsoft and seemed easy to get started with. But here is an overview of some other LLM Agent frameworks or platforms you can further explore.
-
LangChain is a leading framework designed for building applications powered by language models, focusing on chaining calls to LLMs and integrating various data sources and APIs.
-
CrewAI is a framework aimed at streamlining AI application development, emphasizing collaboration among AI agents and human users to solve complex problems through multi-agent systems.
-
AutoGen is focused on automating the generation of code and content using LLMs, reducing development time by automating repetitive coding tasks and enhancing productivity.
| Feature/Framework | LangChain | CrewAI | AutoGen |
|---|---|---|---|
| Focus | Building applications with LLMs | Collaboration among AI agents and users | Automating code and content generation |
| Key Strengths | Chaining LLM calls, integration with APIs | Multi-agent systems, context management | Speeding up development, reducing repetitive tasks |
| Use Cases | RAG systems, complex workflows | Interactive applications, problem-solving | Code generation, documentation creation |
| Target Users | Developers of LLM applications | Teams leveraging AI for collaboration | Developers seeking productivity tools |
| Ease of Use | User-friendly for integrating LLMs | Intuitive for multi-agent environments | Simplifies repetitive coding tasks |
| Documentation | Extensive documentation and community support | Clear guidelines and examples | Detailed guides and examples |
| URL | LangChain | CrewAI | AutoGen |
Demo LLM Agent using AutoGen
In this demo we are going to build a LLM Agent that can provide restaurant recommendations based on location information provided.
Example LLM Agent scenario
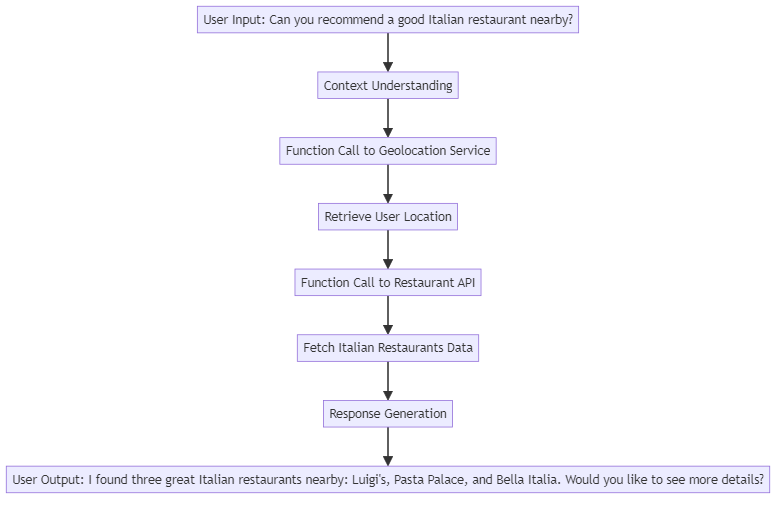
Diagram Explanation:
- User Input: The starting point is the user’s request for a restaurant recommendation.
- Context Understanding: The agent processes and understands the context of the request.
- Function Call to Geolocation Service: The agent requests location data.
- Retrieve User Location: The geolocation service returns the user’s current location.
- Function Call to Restaurant API: The agent queries the restaurant API for information.
- Fetch Italian Restaurants Data: The API returns data on Italian restaurants near the user’s location.
- Response Generation: The agent compiles the information into a user-friendly format.
- User Output: Finally, the agent provides the user with tailored recommendations.
This example illustrates how an LLM agent interacts with the user, processes requests, accesses external resources, and generates meaningful responses in a structured manner.
This restaurant recommendation scenario is an exemplary illustration of an LLM (Large Language Model) agent for several reasons:
-
Complex Task Execution: The process involves multiple sequential steps: understanding the user query, accessing location data, retrieving information from an external restaurant API, and generating a coherent, user-friendly response. This complexity highlights the LLM agent’s ability to manage and orchestrate diverse tasks effectively, showcasing its versatility.
-
Contextual Awareness: The LLM agent demonstrates the ability to comprehend context—a key strength of LLMs. It interprets the user’s request not just as a generic question but as a specific inquiry that requires knowledge of cuisine type and geographical context. This serves to illustrate the advanced natural language understanding capabilities of LLMs.
-
Integration with External APIs: This example emphasizes how LLM agents can call and utilize external services (geolocation and restaurant databases), distinguishing them from simpler rule-based systems. By leveraging real-time data from external sources, LLM agents can provide more accurate and relevant information, enhancing their functionality.
-
Personalization: The agent’s capability to provide tailored suggestions based on user preferences and current location exemplifies a key advantage of LLMs: their potential for personalization. This enriches the user experience by making responses more relevant and engaging.
-
Iterative Response Interaction: The scenario allows for further interaction—after the agent provides recommendations, it prompts the user for additional engagement (e.g., asking if the user wants more details). This feature showcases the conversational nature of LLM agents and their ability to maintain a fluid dialogue with users.
In summary, this restaurant recommendation example tries to show the essence of LLM agents by showcasing their capability to understand context, execute complex tasks, leverage external APIs, deliver personalized experiences, and maintain interactive dialogues—all vital characteristics that highlight the potential and utility of LLM agents in real-world applications.
Here is animated gif demonstrating the LLM Agent making restaurant recommendations.
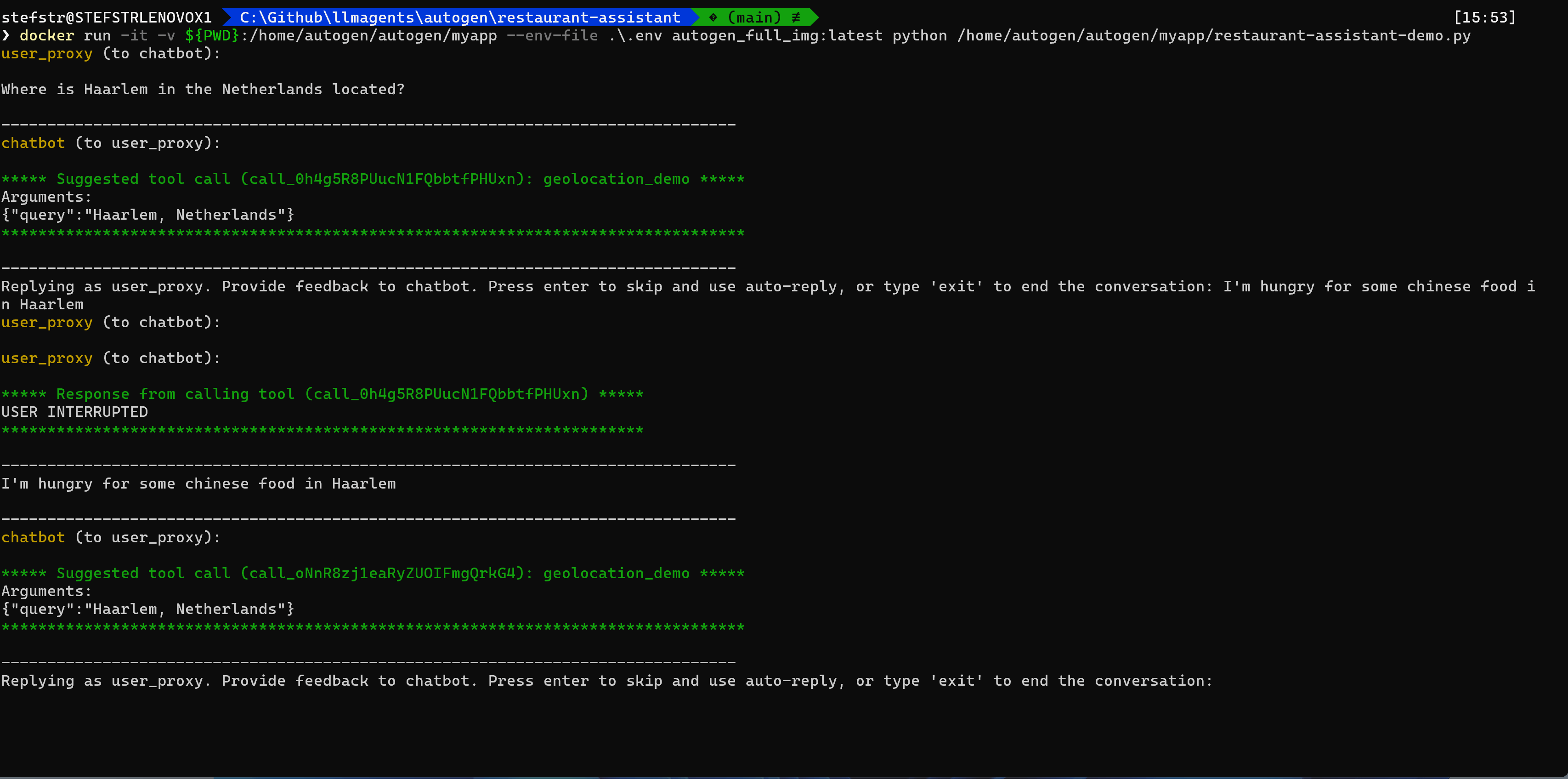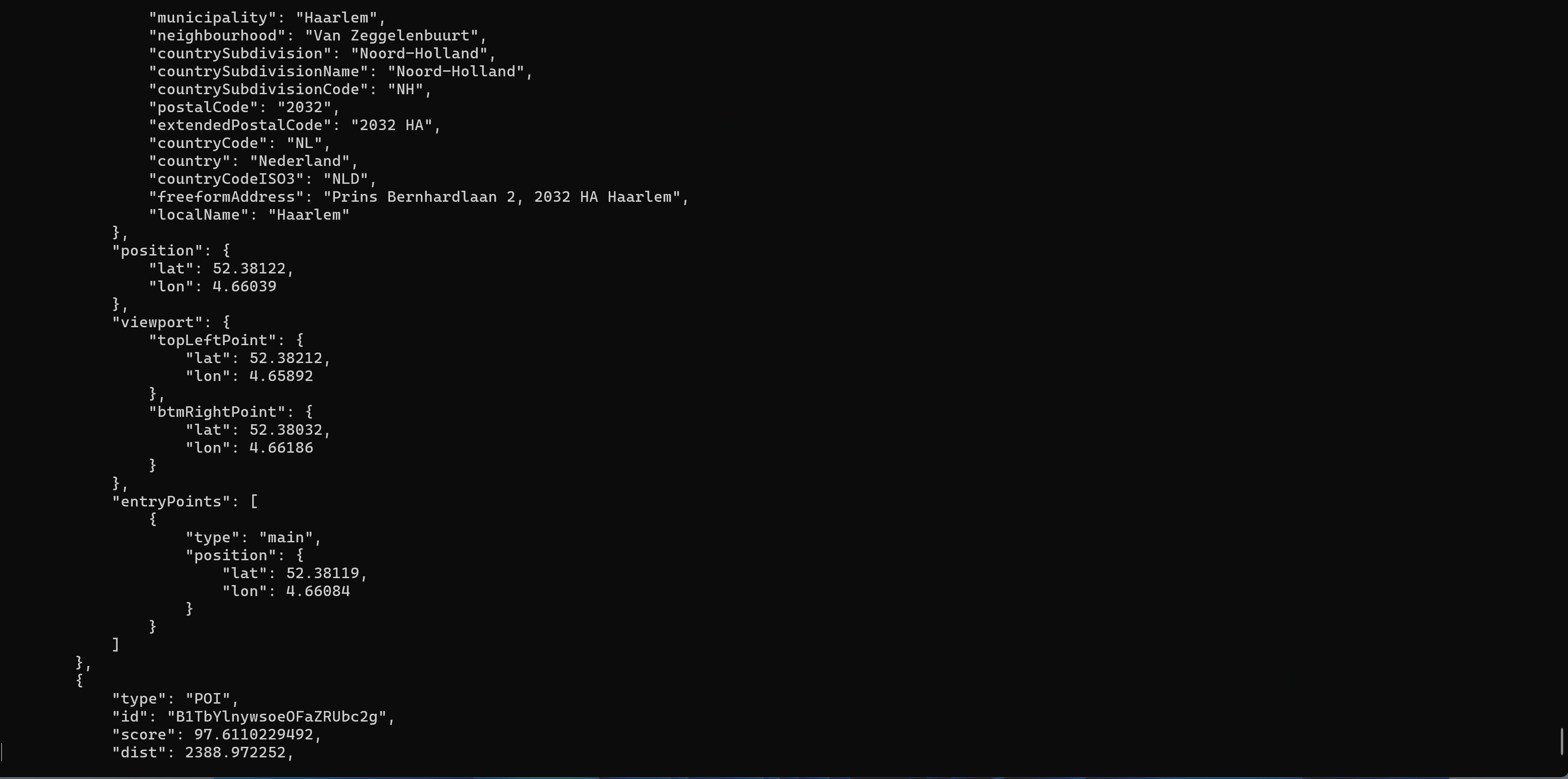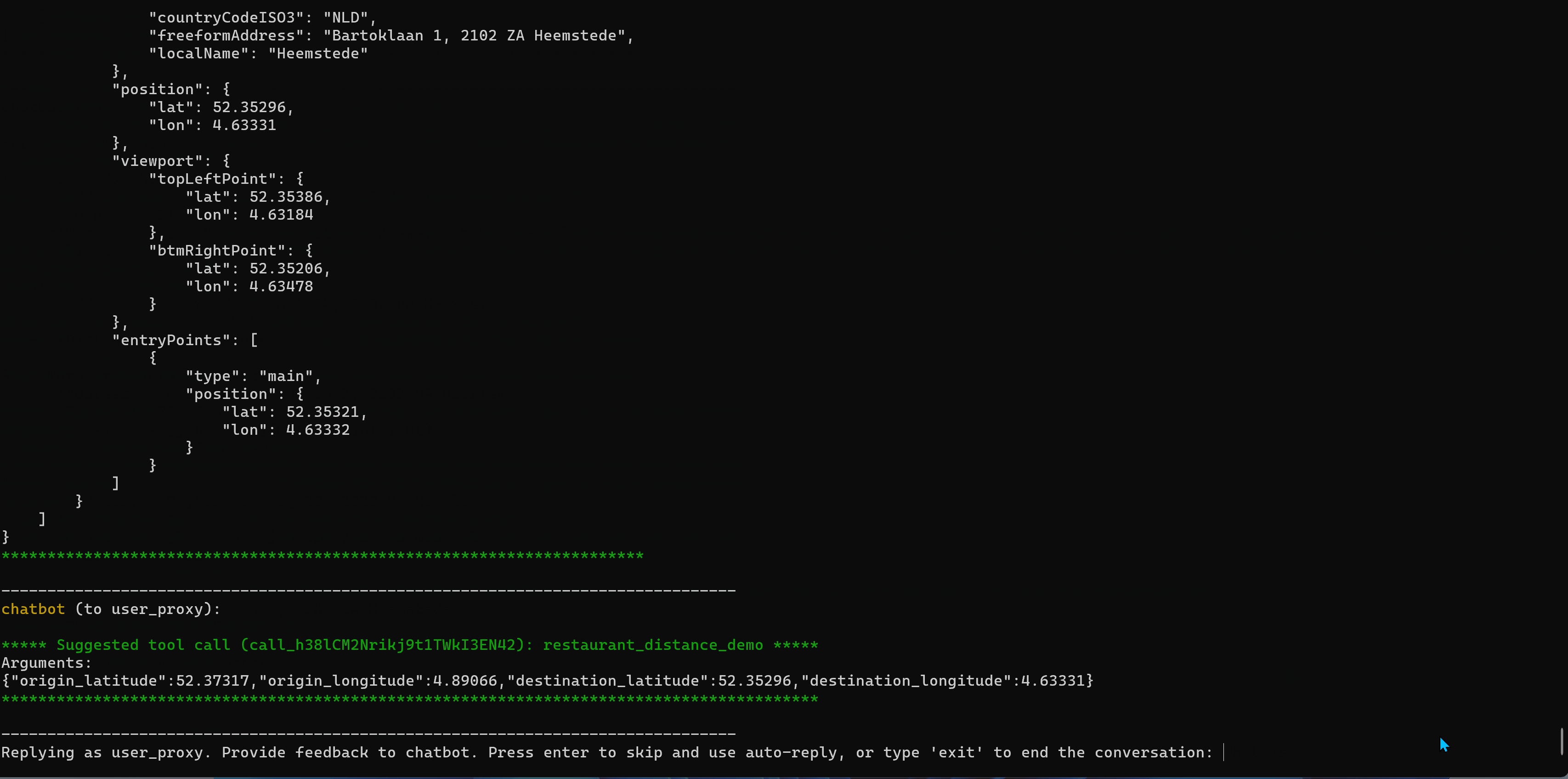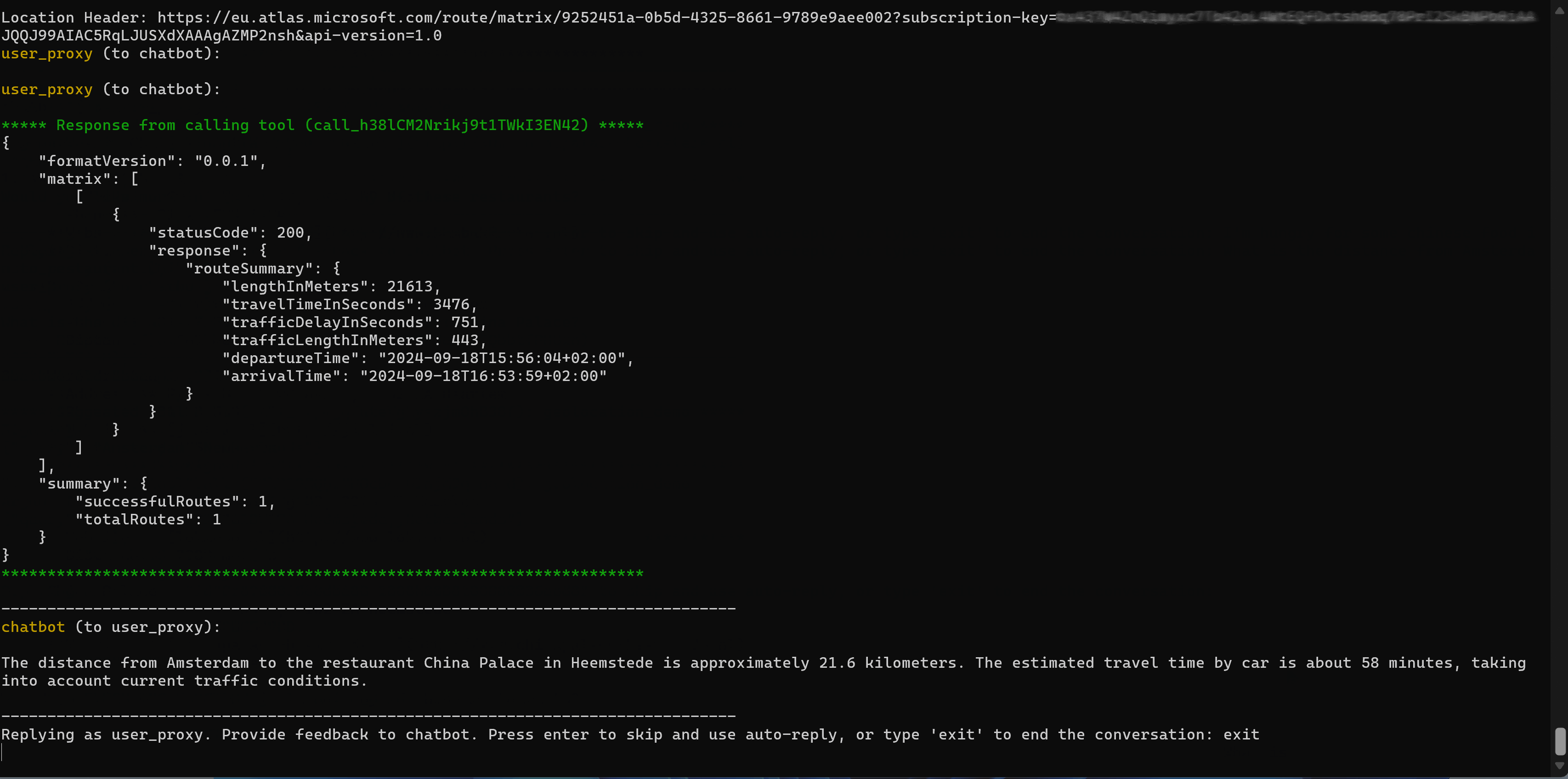
If you want to see this in action yourself here is a link to the information to get this running in your own environment.
For this the following prerequisites are required:
- Azure Subscription with access to Azure Maps and AI services.
- Docker (for Windows).
- AutoGen LLM Agent Platform (included in Docker image)
- API keys for Azure Maps and Azure OpenAI.
Conclusion
LLM Agents are changing how we use technology in our daily lives. They are designed to understand and respond to our requests, making tasks easier and more efficient. One of the best parts about these agents is how simple they are to develop, especially with frameworks like AutoGen that streamline the process.
Function calling stands out as a key feature that allows these agents to interact with other tools and services in real time. This means that LLM Agents can gather accurate information, perform specific actions, and provide relevant responses that fit the user’s needs. By combining natural language understanding with the ability to call functions, LLM Agents can handle a wide range of tasks effectively.
Hope you enjoyed this introduction to LLM Agents and are interested in exploring them in more detail yourself.
Below some references for further reading.
References:
-
From LLMs to LLM-based Agents for Software Engineering: A Survey of …
This paper discusses challenges addressed by LLM-based agents, combining LLM strengths with external tools for dynamic operations. It covers advancements like Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG). -
LLM Agents: The Ultimate Guide - SuperAnnotate
This guide details LLM agents, their benefits, capabilities, and practical examples in language model applications, showcasing their ability to solve complex issues through data analysis and strategic planning. -
Introduction to LLM Agents | NVIDIA Technical Blog
This blog demystifies LLM-powered agents, defining them as systems that leverage LLMs to reason and plan solutions to problems, employing tools like RAG and memory for improved responses. -
Exploring Autonomous Agents through the Lens of Large Language Models …
This paper provides a comprehensive overview of LLM-based autonomous agents, including their architecture, evolution, and applications. -
LLM Agents — Intuitively and Exhaustively Explained
This article focuses on the concept of agents that empower language models to reason and interact, with a practical approach to implementing agents using tools like LangChain. -
Everything You Need to Know About OpenAI Function Calling
This article discusses how to build a custom AI chatbot using OpenAI’s function calling tools and explores its various applications. -
Practical Examples of OpenAI Function Calling
This post provides a clear guide to leveraging OpenAI function calling in Python to generate structured outputs from AI. -
Function Calling - OpenAI API
This official documentation outlines the use cases for function calling in the OpenAI API, including how it enables assistants to fetch data and take actions based on user inputs. -
The LLM Series #2: Function Calling in OpenAI Models: A Practical Guide - Towards AI.
This article provides insights into how function calling enhances efficiency and flexibility in OpenAI models, allowing for the handling of complex tasks. -
Function Calling in the OpenAI API - OpenAI Help Center
This help article explains how function calling allows connection between LLMs and external tools, enhancing the capabilities of AI assistants. -
What’s an agent?
Blog post from Autogen explaining what they see as an agent. -
How to Set Up AutoGen Studio with Docker
Blog post how to setup AutoGen Studi with Docker. AutoGen Studio is a low-code interface built on top of the AutoGen framework for rapid prototyping of AI agents and multi-agent solutions. -
AI Agent Observability with Langfuse
The blog post “AI Agent Observability with Langfuse” discusses how Langfuse integrates with Llama Agents to automatically capture traces and metrics, enhancing the monitoring and management of multi-agent AI systems.